
Levels of ecological organization. Human Activity that changes Abiotic and Biotic Factors
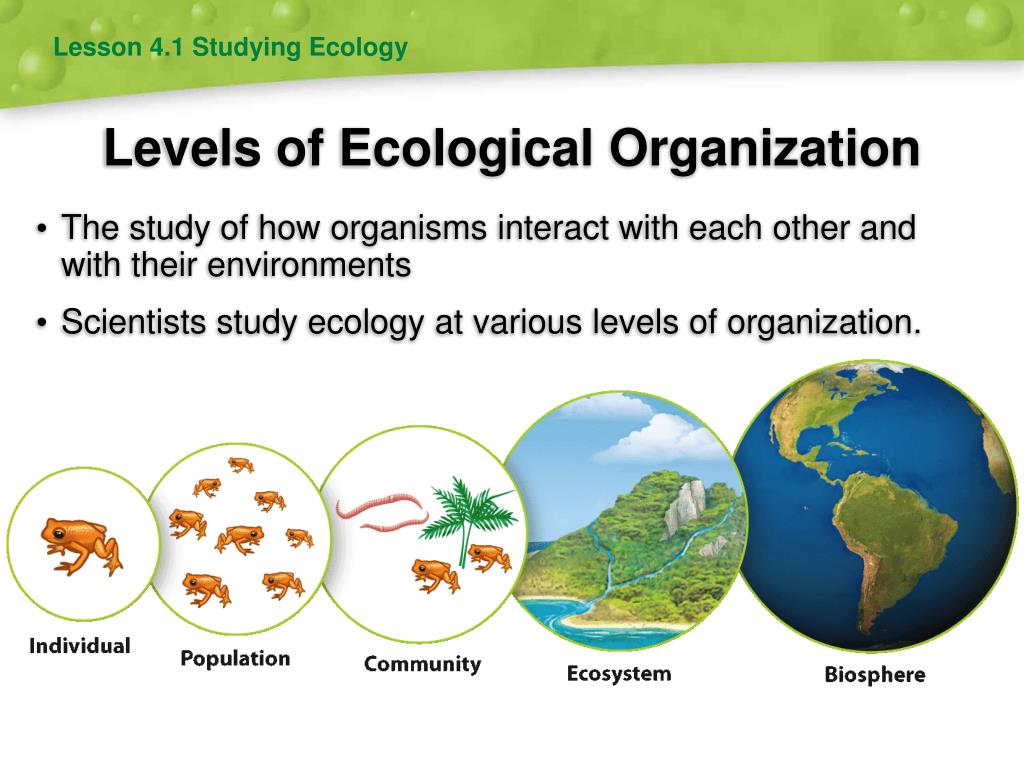
Figure 44.1 A. 1: Levels of ecological study: Ecologists study within several biological levels of organization, which include organism, population, community, and ecosystem. interactions, interrelationships, behaviors, and adaptations of organisms. the movement of materials and energy through living communities.
PPT Ecological Levels of Organization PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5442069
It includes land, water, and even the atmosphere to a certain extent. Taken together, all of these levels comprise the biological levels of organization, which range from organelles to the biosphere. Figure 1.8.1 1.8. 1: Biological Levels of Organization: The biological levels of organization of living things follow a hierarchy, such as the one.

The basic unit of ecological hierarchy exhibits which of the following attributes?
Google Classroom Overview of ecology. Biotic and abiotic factors. The different levels of ecology. Key points Ecology is the study of how organisms interact with one another and with their physical environment.

PPT Principles of Ecology PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4860436
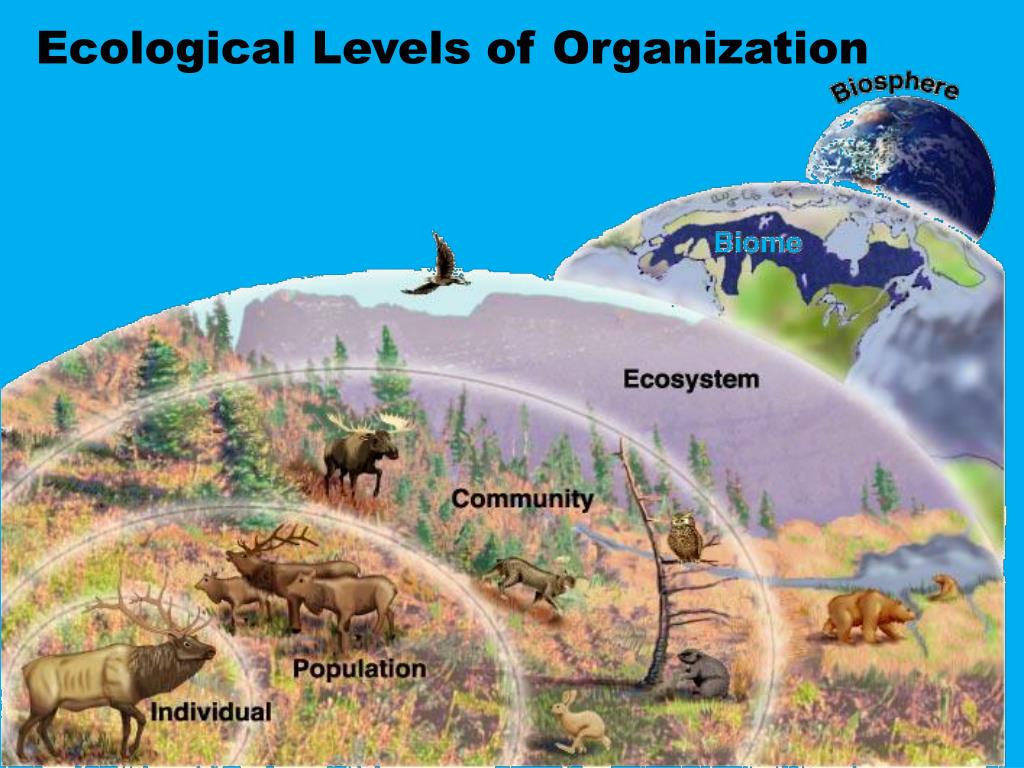
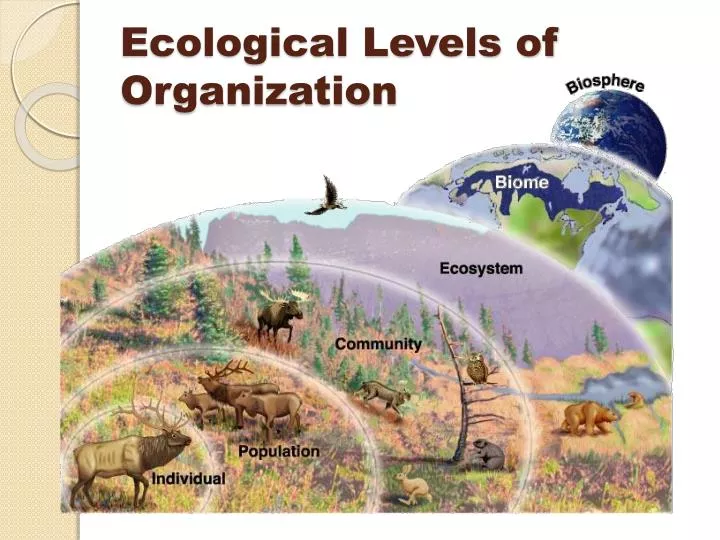
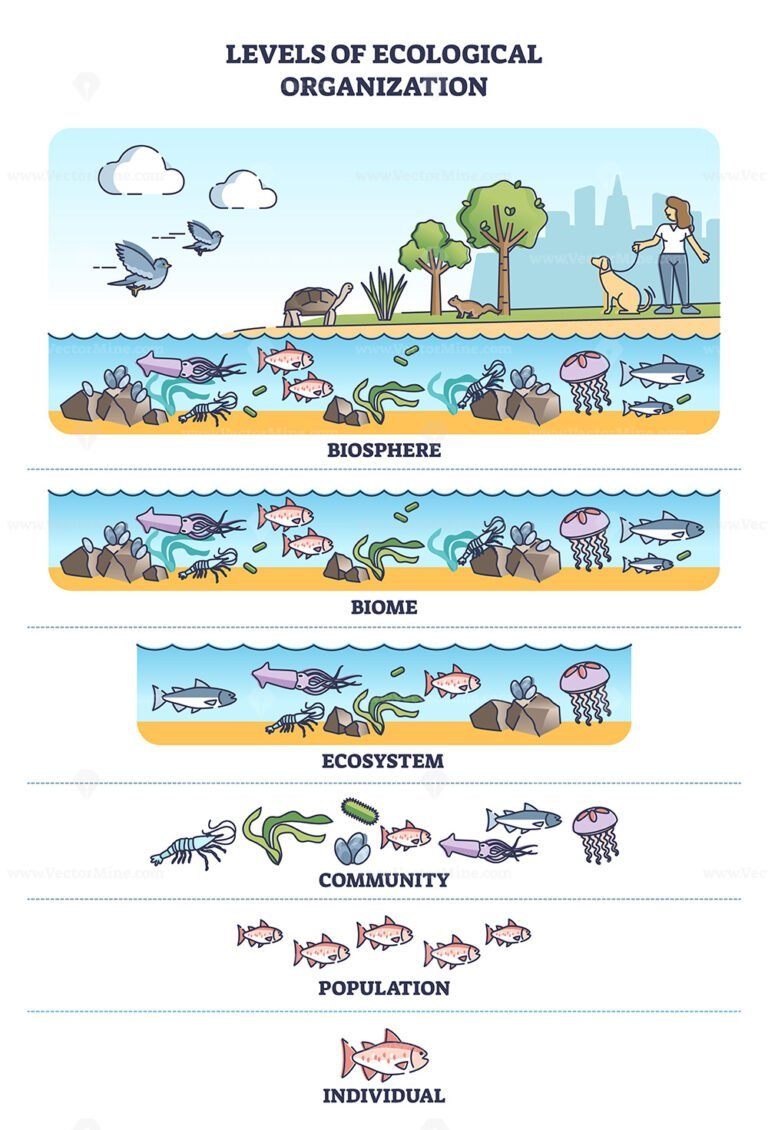
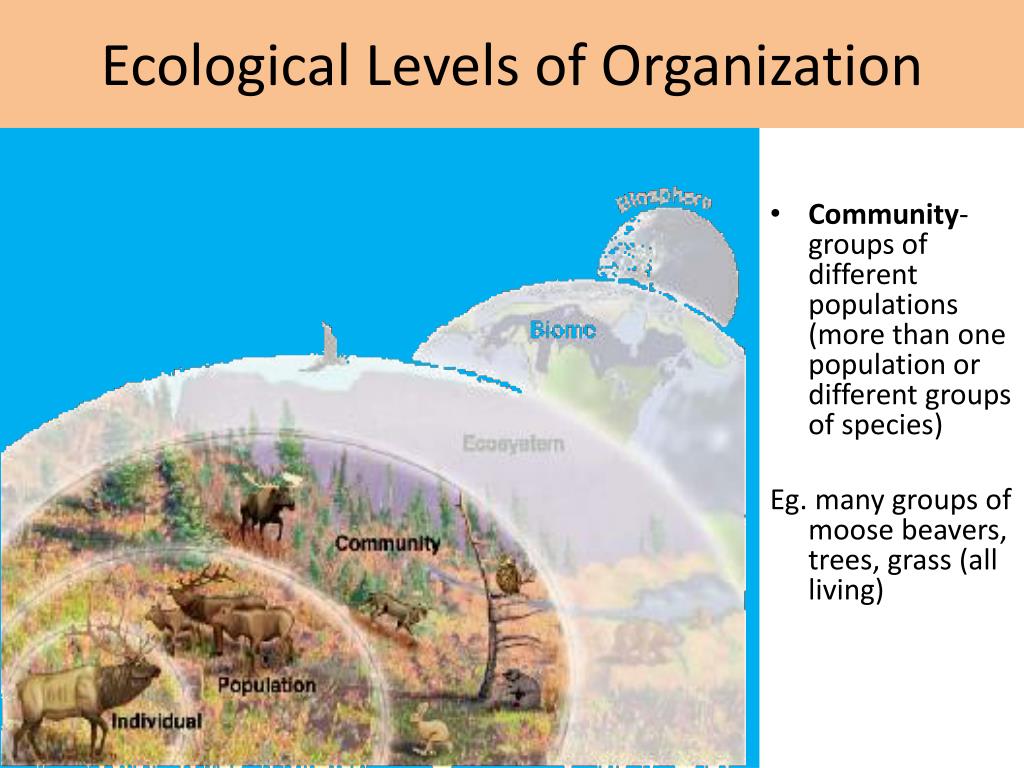
Ecological organization level 1: individuals or organisms - with examples Ecological organization level 2: population - with examples Ecological organization level 3: community - with examples Ecological organization level 4: ecosystem - with examples Ecological organization level 5: biome - with examples

Levels of Ecological Organization Definition, Examples
Here are the levels of organisation, from the smallest to the largest: Organism → Population → Community → Ecosystem → Biome → Biosphere Ecological Level 1 - Organisms It is the simplest level of organisation, which includes both organisms with one cell and organisms with more than one cell.
PPT Ecological Levels of Organization PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3723430
Ecological Hierarchy. Studying all living things and their environments would be a huge undertaking. Generally, the study of ecology is made more manageable by organizing the biological world into a nested hierarchy. Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\): This figure shows levels of organization in nature, from the individual organism to the biosphere.
Levels of ecological organization with organism division outline diagram VectorMine
The diagram above will hopefully help you visualize how the different ecological levels are related to each other. Individuals make up a population; populations make up a species; multiple species and their interactions make up a community; and multiple species and their interactions make up ecosystems when you include the abiotic factors.

6 Levels of Ecological Organization From Largest to Smallest
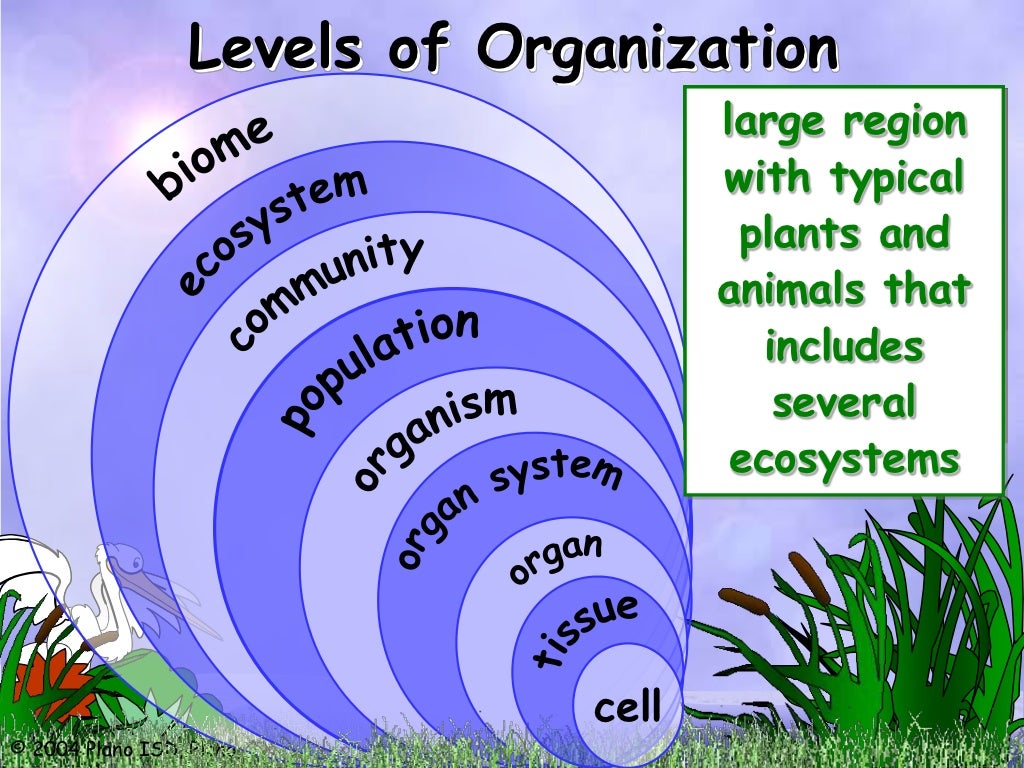
What Are the 6 Levels of Organization in Ecology? Biological organization is a hierarchy of complex biological structures and systems, ranging from atoms at the lowest level to biosphere at the highest, which are used to define life by resorting to what is referred to as the reductionist approach.

PPT Ecosystems What Are They and How Do They Work? PowerPoint Presentation ID2331592
Within the discipline of ecology, researchers work at four specific levels, sometimes discretely and sometimes with overlap: organism, population, community, and ecosystem (Figure 1). Figure 1. Ecologists study within several biological levels of organization.

PPT Rangeland Ecology PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2864060
Ecological Levels of Organization: Definition | Vaia Biology Heredity Ecological Levels of Organization Ecological Levels of Organization Picture the Earth. The Earth is a gigantic place, isn't it? Now imagine zooming in. You might picture mountain ranges and oceans.
Ecosystems, biotic and abiotic factors
1. INTRODUCTION. Ecological interactions affect key aspects of biodiversity across all levels of organization (Levin 1992, Margalef 1963).Individuals are the basic interacting units of ecological systems, and their interactions affect the demography (MacArthur & Levins 1967) and evolution of populations (Benkman 1999).These ecological interactions among individuals in turn connect populations.
PPT Ecological Levels of Organization PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5442069
The Levels of ecological organization Are individual, population, community, ecosystem, biosphere and biome. They describe the disposition of biological organisms in relation to each other, being a classification and organization of the various ecosystems. These ecosystems can be studied in small or large levels.

Levels Of Organization Ecology slidesharedocs
The following points highlight the seven major ecological levels of organisations. The ecological levels are: 1. Organisms 2. Population 3. Biological Community 4. Ecosystem 5. Landscape 6. Biome 7. Biosphere. Ecological Level # 1. Organisms: They make the basic unit of study in ecology.
Levels Of Organization Ecology slidesharedocs
S3 Revised: Levels of Organization in the Ecosystem - 7th grade 1 Levels of Organization in the Ecosystem Lesson Overview In this lesson, students will examine and analyze various ecosystem components to identify and evaluate ecological concepts such as biotic and abiotic factors, species, populations, communities, ecosystems, and biomes.

Levels of organization in an Ecosystem • Teacha!
There are five levels of organization in the ecosystem. They are arranged from smallest to largest in the following order: Levels of Ecological Organization. 1. Organism. It is the lowest level of organization in an ecosystem. An organism or individual is a single organism, plant, animal, or microorganism, such as bacteria and fungi, capable of.
6 Different Levels Of Organization That Ecologists Study Study Poster
2.1: Levels of Ecology. Ecology covers a vast range of topics and can be viewed on multiple levels. One level is that of the individual organism — a single bacterium, an individual wolf pup. This includes individual behavior and physiology, with behavior as part of ecology. Population ecology covers groups of organisms of the same species—a.